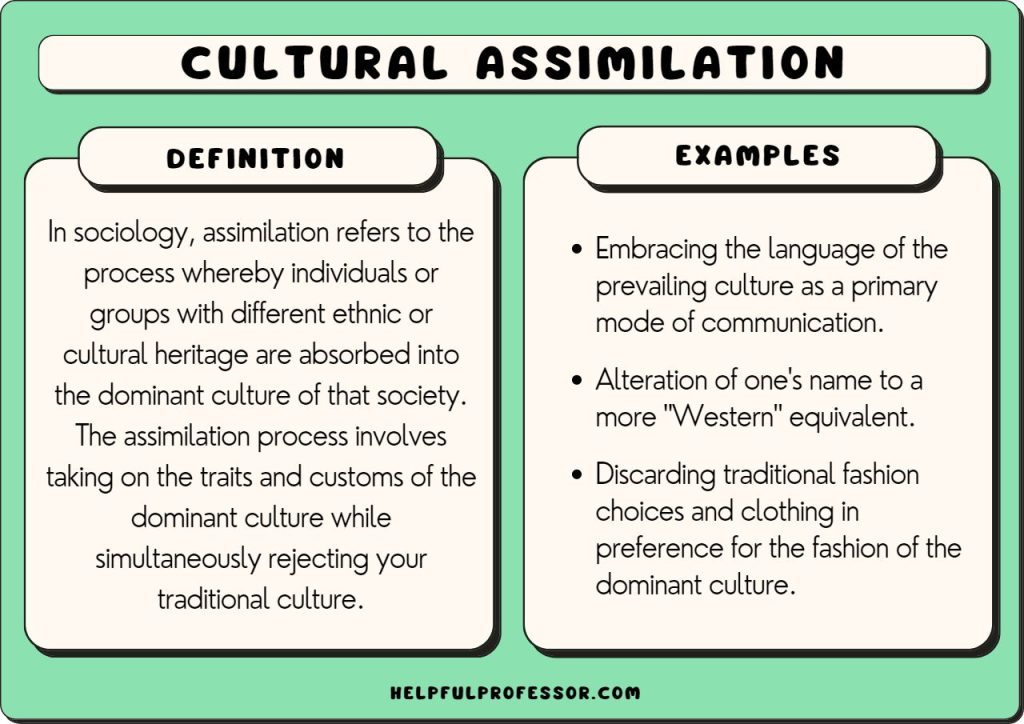
Have you ever wondered about cultural assimilation and what it means? Cultural assimilation refers to the process where one culture adopts or absorbs elements of another culture. It’s an interesting concept that helps shape societies around the world. In this article, we’ll dive into examples of cultural assimilation and explore its significance in our increasingly interconnected world.
Cultural assimilation can be seen in various forms, such as language, religion, traditions, and even food. It’s a dynamic process that occurs when different cultures come into contact with each other. By understanding these examples, we can better appreciate the diversity and interconnectedness of our global society.
So, what are some examples of cultural assimilation? Join us as we explore the fascinating world of cultural exchange and uncover the answer to the question, “Which of the following is an example of cultural assimilation?” Let’s embark on this journey together and discover the power of cultural interaction.
Which of the Following Is an Example of Cultural Assimilation?
Cultural assimilation refers to the process by which individuals or groups from one culture adopt the customs, beliefs, and behaviors of another culture. In today’s diverse and interconnected world, cultural assimilation has become a prominent topic of discussion. People are often curious about the different ways in which cultures merge and the impact of assimilation on society. In this article, we will explore various examples of cultural assimilation and delve into the complexities and implications of this phenomenon.
1. Language Acquisition as a Form of Cultural Assimilation
Language plays a crucial role in cultural assimilation. When individuals or communities adopt a new language as their primary mode of communication, it is a significant example of cultural assimilation. This process is often observed in immigrant communities, where individuals learn the language of their host country to integrate into society and access educational and employment opportunities.
Language acquisition can lead to a deeper level of assimilation as individuals begin to think and express themselves using the new language. This linguistic assimilation not only facilitates communication but also helps in understanding and embracing the values, traditions, and nuances of the new culture. However, it is vital to strike a balance between preserving one’s native language and embracing the language of the host culture to maintain a cultural connection while assimilating.
2. Clothing and Fashion as Cultural Assimilation
Clothing and fashion choices are significant aspects of cultural identity. However, they can also act as indicators of assimilation. When individuals or communities adopt the clothing styles and fashion trends of the dominant culture, it can be seen as a form of cultural assimilation.
For instance, consider the popularity of Western clothing styles such as jeans, suits, and dresses around the world. This widespread adoption of Western fashion represents a visible example of cultural assimilation as people integrate elements of Western culture into their own personal style.
It is essential to note that clothing choices may not always reflect complete assimilation. Individuals may incorporate elements of the dominant culture while still preserving and celebrating their cultural heritage through traditional garments and accessories. This fusion of cultural influences can lead to the creation of unique and diverse fashion trends.
3. Food and Cuisine as Cultural Assimilation
Food is a universal language that transcends borders and brings people together. Cultural assimilation through food can be observed when individuals or communities adopt the culinary traditions, ingredients, and flavors of another culture.
The globalization of food has contributed to increased cultural assimilation in this aspect. Restaurants serving dishes from different cultures, fusion cuisines, and the availability of ingredients from around the world have made it easier for people to explore and incorporate diverse food traditions into their diets.
When individuals embrace and enjoy foods from different cultures, it not only reflects assimilation but also promotes cultural exchange and appreciation. It allows individuals to broaden their palates, learn about different traditions, and foster a sense of unity amidst diversity.
Additional Aspects of Cultural Assimilation:
4. Education and Academic Assimilation:
Education plays a significant role in cultural assimilation. When individuals from different cultural backgrounds enroll in educational institutions, they are exposed to the values, norms, and educational systems of the host culture. This exposure can reshape their perspectives and facilitate assimilation into the larger society.
5. Social and Relational Assimilation:
Social and relational assimilation occurs when individuals form relationships and connections with members of the dominant culture. Interacting with people from the host culture allows for the exchange of ideas, traditions, and customs, leading to a greater understanding and integration into society.
6. Workplace Assimilation:
The workplace is another significant arena for assimilation. When individuals join the workforce, they often need to adapt to the expectations, norms, and practices of the workplace culture.
By being aware of these aspects of cultural assimilation, individuals and communities can navigate the process while preserving their own identities and contributing to a diverse and inclusive society. Cultural assimilation can be a complex and nuanced phenomenon, and it is essential to cultivate an understanding and appreciation for the various ways in which cultures merge and evolve.
Key Takeaways: Which of the Following Is an Example of Cultural Assimilation?
- Cultural assimilation refers to the process in which individuals or groups adopt the culture of another society.
- An example of cultural assimilation is when immigrants adapt to and adopt the customs, language, and traditions of their new country.
- Cultural assimilation often occurs when there is integration and interaction between different cultures.
- Cultural assimilation can lead to a loss of one’s original culture and the formation of a new blended culture.
- Cultural assimilation can be both voluntary and involuntary, depending on the circumstances and pressures individuals face.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on cultural assimilation!
Here are some common questions and answers related to the topic:
Q: What is cultural assimilation?
Cultural assimilation refers to the process where individuals or groups adopt the cultural practices and values of a dominant society. It involves blending or integrating into a new culture, often leading to the loss or modification of one’s original cultural identity. This can happen voluntarily, as individuals actively choose to adopt new cultural norms, or it can be a result of social, political, or economic pressures.
For example, when a person immigrates to a new country and embraces the traditions, language, and lifestyle of that country, they are undergoing cultural assimilation. It is important to note that cultural assimilation is a complex and multifaceted process with both positive and negative consequences.
Q: What are some examples of cultural assimilation?
There are several examples of cultural assimilation throughout history and in different parts of the world. One example is the forced assimilation of Native American tribes in the United States during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Native children were taken from their families and sent to boarding schools where they were forced to abandon their languages, traditions, and cultural practices in order to assimilate into mainstream American society.
Another example is the historical assimilation of different immigrant groups into the United States. In the early 20th century, immigrants from various countries, such as Italy, Ireland, and Poland, faced pressure to assimilate into American culture. This often meant adopting English as their primary language, adopting American customs, and integrating into mainstream society while leaving behind aspects of their native cultures.
Q: What are the benefits of cultural assimilation?
Cultural assimilation can have various benefits for individuals and societies. For individuals, it can provide opportunities for social mobility, economic advancement, and a sense of belonging in a new community. Assimilating into a new culture can also help individuals navigate the challenges of living in a different society, such as accessing education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.
On a larger scale, cultural assimilation can contribute to social harmony, multiculturalism, and national unity. When different cultural groups come together and adopt common values and practices, it can foster understanding, cooperation, and peace among diverse communities. Cultural assimilation can also lead to the development of new cultural forms and expressions, enriching the overall cultural landscape of a society.
Q: What are the challenges of cultural assimilation?
Cultural assimilation is not without its challenges and drawbacks. One of the main challenges is the potential loss or suppression of one’s cultural identity and heritage. When individuals are pressured to conform to the dominant culture, they may feel a sense of alienation, disconnection, or even shame about their own cultural background. This can lead to a loss of cultural diversity and the erosion of unique cultural traditions.
Additionally, cultural assimilation can perpetuate power imbalances and inequalities within societies. It can marginalize minority cultures, reinforce discrimination, and lead to the erasure of indigenous or minority voices. Assimilation may also result in the loss of language diversity, as languages other than the dominant language become less commonly spoken or even extinct.
Q: How can cultural assimilation be approached in a more inclusive manner?
To approach cultural assimilation in a more inclusive manner, it is important to recognize and respect the value of diverse cultural identities. Instead of promoting assimilation as a one-way process, efforts can be made to foster intercultural dialogue, mutual understanding, and the celebration of different traditions. Emphasizing cultural exchange and appreciation can help maintain cultural diversity while promoting social integration.
Encouraging language preservation, supporting multicultural education initiatives, and creating spaces for cultural expression can also contribute to a more inclusive approach to assimilation. It is important to strike a balance between preserving one’s cultural roots and embracing the features of the new culture. This allows individuals to maintain a sense of identity while also participating in and contributing to the broader society.
What is Cultural Assimilation?
Summary:
So, to sum it all up, cultural assimilation is when a person or group adopts the customs, language, and traditions of another culture. It usually happens when people from different backgrounds interact and learn from each other.
In this article, we discussed different examples of cultural assimilation, such as learning a new language, celebrating holidays from another culture, and adopting new customs. We also explored how cultural assimilation can be positive, promoting understanding and unity among diverse groups, but it can also have negative consequences if it leads to the loss of one’s own cultural identity.
Remember, cultural assimilation is a natural part of being in a diverse world, but it’s important to embrace and respect our own culture while appreciating and learning from others. By doing so, we can all contribute to creating a more inclusive and harmonious society where everyone feels valued and accepted. So, let’s celebrate our differences and learn from one another!
