If you’ve ever wondered about economic globalization and its impact on the world, you’re in the right place! So, “Which Three of the Following Are Examples of Economic Globalization”? Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating topic together.
Imagine a world where goods, services, and ideas flow freely across borders, connecting people from different countries and cultures. That’s economic globalization in a nutshell!
In this article, we’ll discuss three specific examples that demonstrate the power and influence of economic globalization. Get ready for a journey that will expand your horizons and show you just how interconnected our world truly is. Let’s get started!
Which Three of the Following Are Examples of Economic Globalization?
In today’s interconnected world, economic globalization plays a significant role in shaping economies worldwide. The integration of economies across borders through trade, investment, and the exchange of goods and services has led to profound changes in the way countries interact and conduct business. This article will explore various examples of economic globalization and highlight three key areas where its impact is most evident.
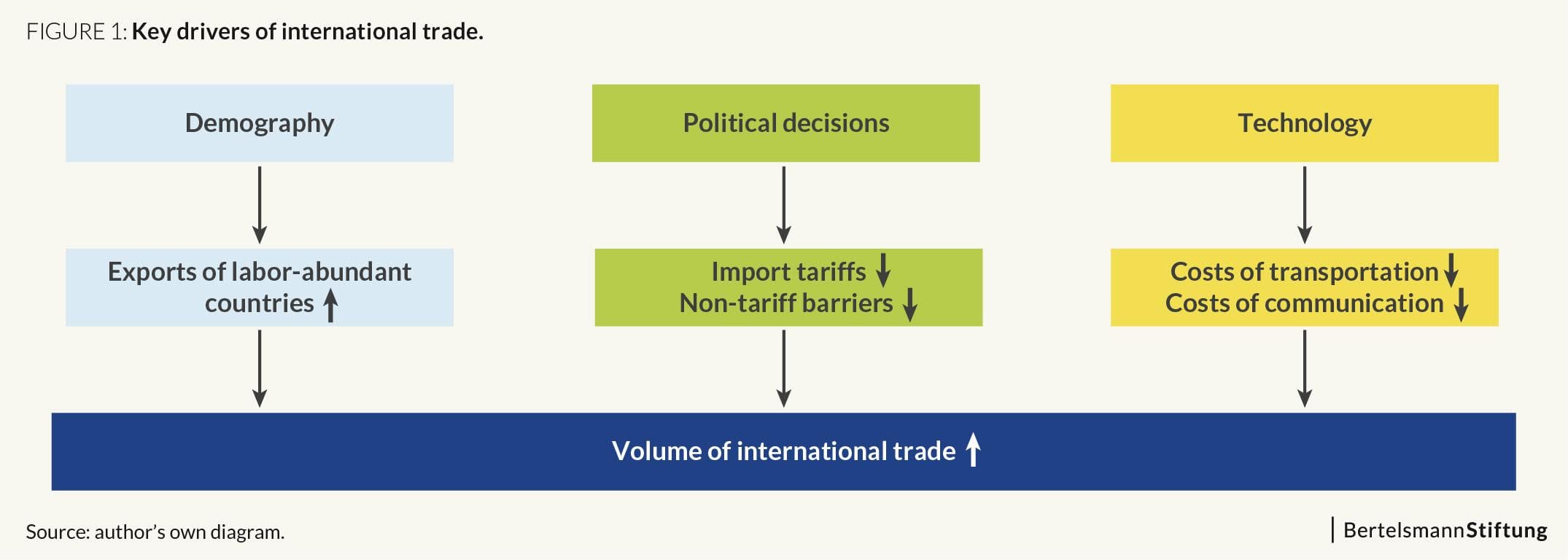
1. International Trade
One of the primary drivers of economic globalization is international trade. The exchange of goods and services between countries has greatly expanded over the years, facilitated by advancements in transportation and communication. Today, products from different corners of the world can be found on supermarket shelves, highlighting the extensive global trading networks that have been established. Global companies, such as Apple and Samsung, rely on global supply chains to source components from different countries and assemble their products in locations with competitive advantages. This interdependence of nations through trade has opened up new markets, increased consumer choices, and created opportunities for economic growth.
Moreover, trade agreements and organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) have played a vital role in promoting international trade and reducing trade barriers. Tariff reductions and trade liberalization have allowed countries to specialize in the production of goods and services where they have a comparative advantage, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. By participating in global trade, countries can harness their unique strengths and resources, generating income, employment, and economic development.
Benefits of International Trade:
- Increased economic growth and development
- Access to a wider range of goods and services
- Creation of employment opportunities
2. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to the investment made by individuals, companies, or governments in foreign countries to establish business operations or acquire ownership stakes in local enterprises. FDI has become a significant driver of economic globalization, allowing for the transfer of capital, technology, and expertise across borders. Multinational corporations (MNCs) play a crucial role in FDI, seeking opportunities in foreign markets to expand their reach and maximize their profits.
FDI brings numerous benefits to both the host country and the investing country. For the host country, FDI can contribute to economic growth, job creation, and the transfer of skills and technology. It can also help attract further investment, as other companies may be enticed to enter the market due to the presence of established multinational companies. On the other hand, the investing country benefits from access to new markets, cost efficiencies, and the ability to tap into different labor pools and resources.
Benefits of Foreign Direct Investment:
- Transfer of advanced technology and know-how
- Job creation and employment opportunities
- Economic growth and development
3. Global Financial Markets
The globalization of financial markets has revolutionized the way capital is allocated and invested across the globe. With advancements in technology, financial transactions now take place instantly, allowing individuals and institutions to invest and trade in various financial instruments regardless of their geographic location. This has resulted in the integration of financial markets worldwide, enabling capital to flow seamlessly across borders.
Global financial markets provide opportunities for individuals, companies, and governments to access capital, manage risks, and invest in diverse assets. Investors can diversify their portfolios through international investments, reducing their exposure to country-specific risks. Stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange and the London Stock Exchange, facilitate the trading of stocks and securities from companies around the world, promoting global investment and fostering economic growth.
Benefits of Global Financial Markets:
- Capital mobilization and allocation
- Diversification of investment portfolios
- Access to international funding
The Future of Economic Globalization
As we move forward, economic globalization is likely to continue shaping the world economy. Technological advancements, such as the advent of the internet and digital platforms, are further facilitating global trade and financial transactions. However, it’s important to note that economic globalization also faces challenges, such as increasing inequality and the potential for exploitative labor practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, economic globalization has transformed the world economy by promoting international trade, attracting foreign investments, and integrating global financial markets. These three examples illustrate the interconnectedness and interdependence of nations in today’s globalized world. However, as economic globalization continues to evolve, it is essential to address its potential drawbacks and ensure that it benefits all participants in a fair and sustainable manner.
Key Takeaways: Which Three of the Following Are Examples of Economic Globalization?
- Global trade: The exchange of goods and services across different countries, allowing for the international flow of products.
- Foreign direct investment: When companies invest in businesses or assets outside of their home country, promoting economic integration.
- Outsourcing: The practice of hiring workers or obtaining goods and services from other countries, often to take advantage of lower costs or specialized expertise.
- Global supply chains: The interconnected networks of production processes that span multiple countries, enabling efficient global production and distribution.
- International financial flows: The movement of money and capital across borders, including investments, loans, and remittances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our frequently asked questions section on economic globalization! Here, we’ll explore some common queries surrounding the topic and provide comprehensive answers to help you better understand the concept. Economic globalization refers to the increasing economic interdependence of countries through the exchange of goods, services, and capital on a global scale. Let’s dive into the questions!
1. What are some examples of economic globalization?
Some prominent examples of economic globalization include international trade, foreign direct investment (FDI), and global supply chains. International trade involves the exchange of goods and services between countries, where each nation specializes in producing what they can most efficiently. Foreign direct investment occurs when companies invest in new facilities or acquire existing businesses in another country. Lastly, global supply chains refer to the interconnected networks of production, distribution, and consumption that span across multiple countries.
These examples signify how economic globalization has fostered the integration of economies around the world, allowing for increased trade, investment, and cooperation among nations.
2. How does economic globalization impact national economies?
Economic globalization can have various impacts on national economies. On the positive side, it opens up opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological advancements. By participating in global trade and investment, countries can access larger markets, generate higher revenues, and attract foreign investments that stimulate their economies. Moreover, economic globalization provides consumers with a wider range of products and services, often at lower prices.
However, economic globalization also presents challenges. It can lead to increased competition, which may negatively affect domestic industries and workers. Additionally, economic interdependence can create vulnerability, as global economic crises and market fluctuations in one country can quickly spread to others. It is essential for governments to implement policies that maximize the benefits and minimize the risks associated with economic globalization.
3. What role does technology play in economic globalization?
Technology plays a crucial role in facilitating and accelerating economic globalization. Advancements in communication and transportation technologies have made it easier for businesses to connect and engage in transactions across borders. The internet, for instance, enables companies to advertise, sell, and communicate with customers worldwide. Online platforms and payment systems have reduced barriers to international trade.
Moreover, technological innovations have transformed supply chains, making them more efficient and interconnected. Transportation methods have become faster and more reliable, allowing goods to be transported across the globe in a shorter amount of time. This integration of technology in economic activities has fueled the growth of economic globalization and made global connections more accessible and seamless.
4. Are there any drawbacks to economic globalization?
While economic globalization offers numerous benefits, it is not without its drawbacks. One major concern is the potential for increased income inequality both within and between countries. As some regions and industries benefit more from globalization, others may struggle to adapt, leading to job losses and economic disparities. Additionally, environmental sustainability can be compromised as globalization intensifies resource consumption and carbon emissions.
Moreover, there are concerns about the loss of cultural diversity and local traditions as global markets influence consumer preferences and practices. Finally, economic globalization can amplify the power of multinational corporations, potentially leading to monopolistic behavior or exploitative practices. It is crucial to address these challenges by implementing policies that promote equitable distribution of benefits, environmental protection, and cultural preservation.
5. How does economic globalization impact developing countries?
Economic globalization can have both positive and negative impacts on developing countries. On one hand, it presents opportunities for growth and development by providing access to larger markets, investments, and technology transfer. Increased trade can boost exports and generate much-needed foreign exchange. Additionally, globalization can attract foreign direct investment, creating job opportunities and stimulating economic activity.
However, developing countries may face challenges as well. They may struggle to compete with advanced economies due to limited resources, technological gaps, and weaker institutional capacity. The potential for increased inequality and negative environmental impacts can also be more pronounced in developing countries. It is crucial for governments and international organizations to support developing nations in harnessing the benefits of economic globalization while mitigating the associated risks.
Examples of Globalization
Summary
So, what have we learned about economic globalization? It’s all about how countries around the world are connected through trade and money. We talked about three examples of economic globalization: international trade, foreign direct investment, and global supply chains.
International trade is when countries buy and sell goods and services to each other. It helps countries access things they don’t have and makes the world more interconnected.
Foreign direct investment is when companies from one country invest in businesses in another country. It helps create jobs and brings in new ideas and technologies.
Global supply chains are like a big puzzle, where different parts of a product are made in different countries and then put together. This helps companies make things more efficiently and at a lower cost.
Overall, economic globalization has its pros and cons. It can bring benefits like more choices and better prices for consumers, but it can also mean competition for jobs and harm to the environment. It’s important for countries to find a balance and work together to make globalization fair and sustainable. So, next time you see a product that says “Made in Another Country,” remember that it’s a result of economic globalization at work!
